Tables
Echo provides a model-based Table component which is used to display tabular information. The information displayed within a Table is held externally by a TableModel.
TableModels
A TableModel is an interface with represents the data displayed in a Table. The model interface provides methods to query the number of rows and columns in a dataset, and determine the value at each column/row coordinate. Additionally, the TableModel interface provides a mechanism for registering TableModelListeners, which will be notified by the TableModel when the data within it has changed.
AbstractTableModel: An AbstractTableModel base implementation of the TableModel class is provided within the Echo API to provide features such as TableModelListener-management. Model implementors who derive from AbstractTableModel will only be required to implement three additional methods, getValueAt() which is used to retrieve the values of individual cells, and getColumnCount() and getRowCount() which specify the number of columns and rows in the Table respectively.
DefaultTableModel: Echo also provides a DefaultTableModel class which stores table data as a two-dimensional array. DefaultTableModel provides additional methods for inserting and deleting rows, and will automatically fire TableModelEvents when data is manipulated.
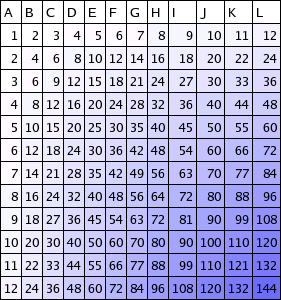
Example: The following AbstractTableModel implementation will produce a 12x12 multiplication table:
class MultiplicationTableModel
extends AbstractTableModel {
public int getColumnCount() {
return 12;
}
public int getRowCount() {
return 12;
}
public Object getValueAt(int column, int row) {
return new Integer((column + 1) * (row + 1));
}
}TableCellRenderers
A TableModel only represents the data contained within a Table. This data may be represented in terms of text strings, integers, boolean values, or arbitrary Java objects. The Table component eventually must display these values in the form of Components. This capability is achieved through the use of a TableCellRenderer.
A TableCellRenderer is used to translate an arbitrary Java object into a Componet. A default implementation is provided by the DefaultTableCellRenderer class, which simply renders any table cell value into an Echo Label component containing the toString() value of the Java object held in the TableModel.
You can create a TableCellRenderer to render model values to any Component desired. You might create a custom renderer to render certain cells as Labels which contained ImageReferences. If a Table was being used for editing information, a TableCellRenderer might render TextFields for String values and CheckBoxes for Boolean values.
Any Components rendered by a TableCellRenderer will be added as children of the Table component. They will be removed and replaced automatically when the TableModel is changed. The Table component is responsible for managing its children; children should never be added or removed from a Table manually.
LayoutData: The TableLayoutData layout data implementation serves to provide a means of customizing the appearance of table cells occupied by rendered Components. TableLayoutData allows the setting of alignment, background color and image, and inset margins of each table cell.
Example: The following code shows a TableCellRenderer which could be used with the previous example TableModel to render
class ValueColorRenderer
implements TableCellRenderer {
public Component getTableCellRendererComponent(Table table,
Object value, int column, int row) {
Label label = new Label(value.toString());
TableLayoutData layoutData = new TableLayoutData();
int colorValue = 255 - ((Integer) value).intValue();
layoutData.setBackground(
new Color(colorValue, colorValue, 255));
label.setLayoutData(layoutData);
return label;
}
}Selection
A Table can be configured to support the selection of rows. Like the ListBox component, Tables can be set up to allow the selection of a single row or multiple rows at one time. Again like ListBox, a Table uses a ListSelectionModel to describe its current selection state.
In order to use selection, a Table must have its selectionEnabled property set to true by invoking the Table.setSelectionEnabled() method. Various methods are provided for configuring the style of the currently selected item, such as Table.setSelectionBackground().
Rollover Effects: Tables provide the capability to set rollover effects whereby rows of the Table are highlighted as the mouse cursor passes over them.
An Example
The following example code creates a Table using the previously shown TableModel example code as its model. The aforementioned TableCellRenderer is configured to render the cells of the Table:
TableModel model = new MultiplicationTableModel();
Table table = new Table(model);
table.setDefaultRenderer(Object.class,
new ValueColorRenderer());
The rendered output: