Building an Application
Now that you've seen the basic concepts, it's time to put them to work. In this section we'll create a simple example application: a number guessing game. The object of the game is for the user to guess a randomly generated integer between 1 and 100 (inclusive) in the fewest number of tries. Each time the user makes an incorrect guess, the application will give the user a hint as to whether the guess was greater than or less than the correct number. When the user correctly guesses the number, a "Congratulations!" message will be displayed and the user will be given the option to play again.
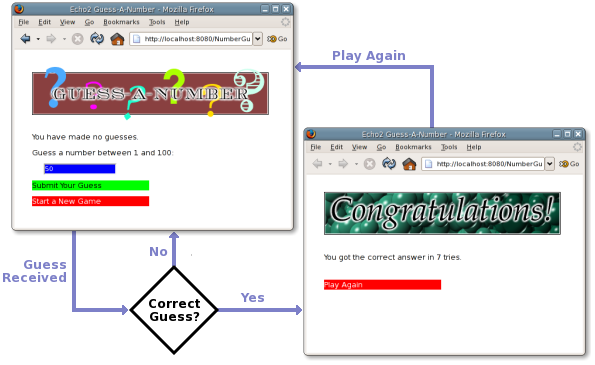
NumberGuessApp, the EchpApp.Application Class
The user interface code of the Guess-A-Number game is divided into three classes, all of which are found in the NumberGuessApp.js source file. The class NumberGuessApp provides the required Echo.Application implementation. The NumberGuessApp.Game and NumberGuessApp.Congratulator classes are both derived from the Echo Column component, and represent the number-guessing and end-of-game screens respectively.
The NumberGuessApp class
/**
* Guess-a-number Tutorial Application.
*/
NumberGuessApp = Core.extend(Echo.Application, {
$construct: function() {
Echo.Application.call(this);
this.startNewGame();
},
/**
* Displays a congratulatory message to the user when s/he
* has guessed the correct number.
*
* @param numberOfTries the number of tries it took the
* user to guess the correct answer.
*/
congratulate: function(numberOfTries) {
this.rootComponent.removeAll();
this.rootComponent.add(new NumberGuessApp.Congratulator(
numberOfTries));
},
/**
* Starts a new game:
* Sets content of Window to a new Game
*/
startNewGame: function() {
this.rootComponent.removeAll();
this.rootComponent.add(new NumberGuessApp.Game());
}
});
State Management: In this example, the NumberGuessApp also serves to manage the high-level state of the application, i.e., starting new games and displaying the end-of-game congratulations message. Two methods have been created to control this state, startNewGame() and congratulate().
Initialization: The constructor of the Echo.Application configures the screen to display a new game by invoking startNewGame(). This method will add a new Game component to the rootComponent object.
Derived Components: The Game and Congratulator classes both extend from Column. Each of these components overrides its constructor to configure itself by creating and adding child Components and setting properties upon instantiation. The practice of extending Components in this fashion is encouraged.
The Game Class
The NumberGuessApp.Game class is a component which handles a single "game session". On construction, a Game generates the secret random number which must be guessed. The constructor adds several components to the Game, including Labels to indicate the status of the game, a TextField into which guessed are entered, and a Button to submit guesses. An additional Button is added to provide the option to reset and start a new game.
Event Handling: The Game class contains two methods which are registered as event listeners, _processGuess() and _startNewGame(). These event handling methods are registered as event handlers with the two buttons. Core.method() is used to create a reference the methods within the Game, such that the this pointer will correctly point to the Game instance when the methods are invoked.
Processing Guesses: The _processGuess() method will first check if the entered guess is wholly invalid, i.e., if the user accidentally entered something other than a number, and displays an error message if necessary by adjusting the text of the _statusLabel. If the guess is in fact a value between 1 and 100, the next question to be answered is whether or not it is correct. If the user has managed to pick the correct number, the congratulate() method of the NumberGuessApp is invoked. Otherwise, the method determines whether the guess was too high or too low and updates the Labels that display the number of guesses made and the prompt message informing the user to make a guess between a range of sensible values.
Handling "New Game" Button Clicks: When _startNewGame() is invoked as a result of the "Start a New Game" button being clicked, it simply calls the startNewGame() method of the Echo.Application, NumberGuessApp. Because Game is a component that is currently part of the hierarchy, we can obtain the application from the this.application property.
The NumberGuessApp.Game class:
/**
* A Column which generates a random number and provides the
* user opportunities to guess it.
*/
NumberGuessApp.Game = Core.extend(Echo.Column, {
/** Randomly generated number between 1 and 100 inclusive. */
_randomNumber: null,
/**
* The current lowest sensible guess, based on previous
* guesses.
*/
_lowerBound: 1,
/**
* The current highest sensible guess, based on previous
* guesses.
*/
_upperBound: 100,
/** The number of guesses made in the current game. */
_numberOfTries: 0,
/** TextField into which guesses are entered. */
_guessEntryField: null,
/**
* Label displaying the current "status".
* Initially blank, this label will inform the user whether
* his/her last guess was too high, too low, or simply
* invalid.
*/
_statuslabel: null,
/**
* Label indicating the total number of guesses made so far.
*/
_countLabel: null,
/**
* Label prompting the user to enter a new guess. The text
* of this label will change as the user makes guesses to
* reflect the updated "sensible" range of possible guesses.
*/
_promptLabel: null,
$construct: function() {
this._randomNumber = Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1;
Echo.Column.call(this, {
insets: 30,
cellSpacing: 10,
children: [
new Echo.Label({
icon: "TitleBanner.png"
}),
this._statusLabel = new Echo.Label(),
this._countLabel = new Echo.Label(),
this._promptLabel = new Echo.Label(),
this._guessEntryField = new Echo.TextField({
background: "#ffffff",
foreground: "#0000ff",
layoutData: {
insets: "0px 20px"
},
events: {
action: Core.method(
this, this._processGuess)
}
}),
new Echo.Button({
text: "Submit Your Guess",
actionCommand: "submit guess",
foreground: "#ffffff",
background: "#008f00",
insets: "3px 10px",
width: 200,
events: {
action: Core.method(this,
this._processGuess)
}
}),
new Echo.Button({
text: "Start a New Game",
foreground: "#ffffff",
background: "#8f0000",
insets: "3px 10px",
width: 200,
events: {
action: Core.method(this,
this._startNewGame)
}
})
]
});
},
/**
* Processes a user's guess.
*/
_processGuess: function(e) {
var guess = parseInt(
this._guessEntryField.get("text"), 10);
if (isNaN(guess)) {
this._statusLabel.set("text",
"Your guess was not valid.");
return;
}
++this._numberOfTries;
if (guess == this._randomNumber) {
this.application.congratulate(this._numberOfTries);
return;
}
if (guess < 1 || guess > 100) {
this._statusLabel.set("text", "Your guess, " +
guess + " was not between 1 and 100.");
} else if (guess < this._randomNumber) {
if (guess >= this._lowerBound) {
this._lowerBound = guess + 1;
}
this._statusLabel.set("text", "Your guess, " +
guess + " was too low. Try again:");
} else if (guess > this._randomNumber) {
this._statusLabel.set("text", "Your guess, " +
guess + " was too high. Try again:");
if (guess <= this._upperBound) {
this._upperBound = guess - 1;
}
}
// Update number of tries label.
if (this._numberOfTries == 1) {
this._countLabel.set("text",
"You have made 1 guess.");
} else {
this._countLabel.set("text", "You have made " +
this._numberOfTries + " guesses.");
}
// Update the prompt label to reflect the new sensible
// range of numbers.
this._promptLabel.set("text",
"Guess a number between " + this._lowerBound +
" and " + this._upperBound + ": ");
},
_startNewGame: function(e) {
this.application.startNewGame();
}
});The Congratulator
The Congratulator is an extremely simple Column which simply displays a "Congratulations!" banner in addition to showing the user how many tries it to took for him/her to successfully guess the secret number. The component provides a single button which may be used to start a new game. Event handling is accomplished using the identical means introduced in the discussion of the Game.
The NumberGuessApp.Congratulator class:
/**
* A Column which presents a congratulatory message to the
* player when the correct number has been guessed.
*/
NumberGuessApp.Congratulator = Core.extend(Echo.Column, {
/**
* A Column which presents a congratulatory message to the
* player when the correct number has been guessed.
*/
$construct: function(numberOfTries) {
Echo.Column.call(this, {
insets: 30,
cellSpacing: 30,
children: [
new Echo.Label({
icon: "CongratulationsBanner.png"
}),
new Echo.Label({
text: "You got the correct answer in "
+ numberOfTries + (numberOfTries == 1
? "try." : " tries.")
}),
new Echo.Button({
text: "Play Again",
foreground: "#ffffff",
background: "#8f0000",
width: 200,
events: {
action: Core.method(
this, this._startNewGame)
}
})
]
});
},
_startNewGame: function(e) {
this.application.startNewGame();
}
});
Initialization
In order to start the application, we must create an initialization method. This method can be named anything you like, but init() is not a bad idea. It should be invoked once the containing web page has been loaded.
The initialization method:
init = function() {
var app = new NumberGuessApp();
var client = new EchoFreeClient(app,
document.getElementById("rootArea"));
client.init();
};
The HTML File
The whole works is housed in an HTML file. The file must include the necessary Echo script files. Additionally, we ensure that standards-mode rendering is enabled by the browser by setting the XHTML 1.0 DOCTYPE and omitting the XML declaration (<?xml version="1.0"?>) which would otherwise (curiously) cause Internet Explorer 6 to enter quirks mode. The init() method is invoked using an onload attribute in the <body> element.
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xml:lang="en" lang="en">
<head>
<script type="text/javascript" src="Core.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="Core.Web.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="Application.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="Render.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="Sync.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="Sync.ArrayContainer.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="Sync.Button.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="Sync.ContentPane.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="Sync.Label.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="Sync.TextComponent.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="Serial.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="Client.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="FreeClient.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="NumberGuess.js"></script>
<title>Number Guess</title>
</head>
<body onload="init();">
<div id="rootArea"></div>
</body>
</html>
